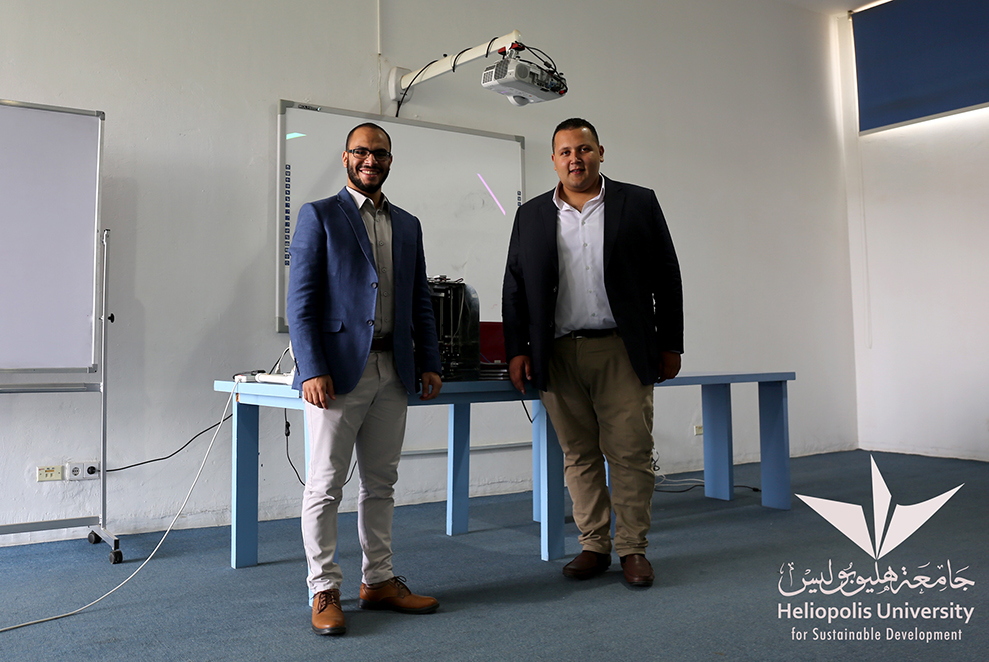
The two winning graduation projects of Heliopolis University were a 3D printer and a robotic human hand. The 3D printer is a machine used to make three-dimensional solid objects. It was developed by two 2017-Engineering graduates: Mohamed Ashraf El Sherbeny and Abdallah Al-Agouz, Department of Mechatronics.
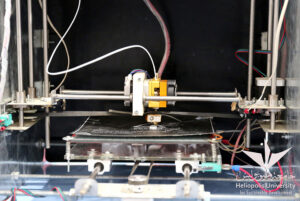 The printing process using this machine starts by creating a 2D computer aided design object. The 2D image is then processed, converting the model into various thin layers. The printer then follows the instructions on the various thin layers to lay down successive layers of material through a print nozzle, called extruder. The extruder moves through its axis to print layer over layer to create the 3D model.
The printing process using this machine starts by creating a 2D computer aided design object. The 2D image is then processed, converting the model into various thin layers. The printer then follows the instructions on the various thin layers to lay down successive layers of material through a print nozzle, called extruder. The extruder moves through its axis to print layer over layer to create the 3D model.
“This 3D printer uses the Stereolithography (SLA) technology” says Mohamed El Sherbeny “It can produce almost any design and hence, it can create many things such as prototypes for products, food wraps, accessories, toys, home decorations, and many others”
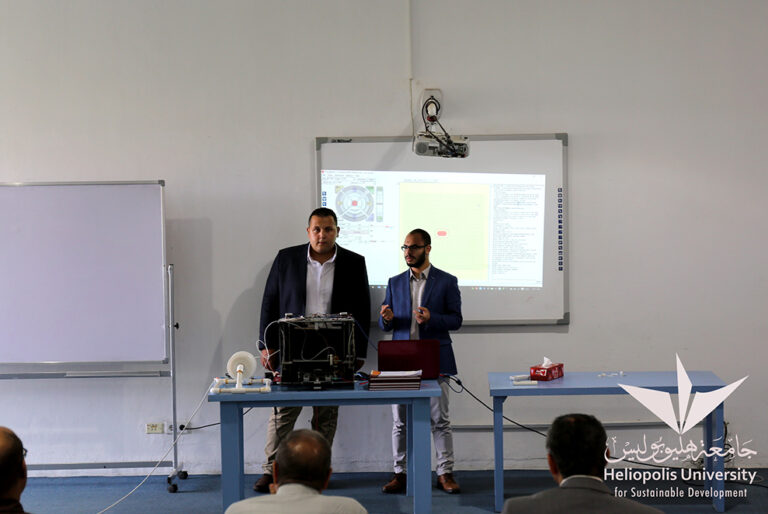


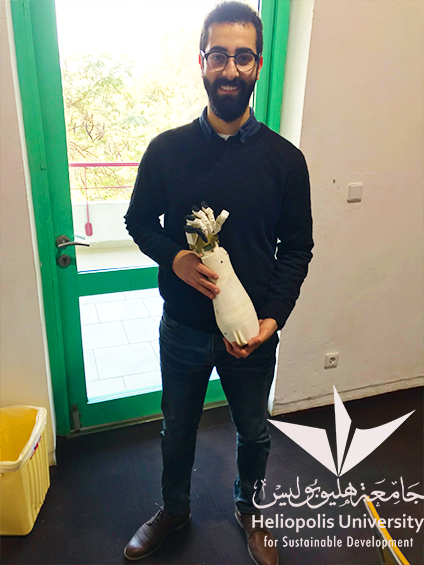
 The second project is about a human hand robot (ROBOQA), controlled via a LeapMotion controller. The robotic hand imitates the movement of the human hand without attaching any sensors to the human hand itself. The project was developed by Mohamed Emad Lotfy, 2017 Engineering graduate, Department of Mechatronics and the parts have been crafted using the above mentioned 3D printer.
The second project is about a human hand robot (ROBOQA), controlled via a LeapMotion controller. The robotic hand imitates the movement of the human hand without attaching any sensors to the human hand itself. The project was developed by Mohamed Emad Lotfy, 2017 Engineering graduate, Department of Mechatronics and the parts have been crafted using the above mentioned 3D printer.
The idea of ROBOQA is based on receiving a signal from the human hand and transferring it to the robotic hand through the LeapMotion controller. The LeapMotion controller transforms the human hand movements into 3D pattern. The Arduino Uno board receives those readings and transmits it to the six servos that are connected to it, which start to move accordingly. Five servos control the fingers of the robotic hand, while the remaining servo rotates the wrist.
“This robotic hand is the first of its type to be developed in Egypt” says Mohamed Emad Lotfy, the developer of ROBOQA. “All robotic hands that were previously developed needed sensors to be attached to the human hand to send signals to the robotic one. However, ROBOQA can remotely imitate the movements of the human hand without any sensors“.
 [:ar]
[:ar]
حصل مشروعا تخرج طلبة كلية الهندسة بجامعة هليوبوليس على المركز الثاني في المسابقة السنوية لمشاريع تخرج الميكاترونيكس والطاقة التي نظمتها جامعة بدر في القاهرة ابريل الماضي. وقد شاركت ١٤ جامعة حكومية وخاصة في المسابقة من خلال ٢٤ مشروعاً للتخرج.
كان مشروعا التخرج الفائزين بجامعة هليوبوليس عبارة عن طابعة ثلاثية الأبعاد ويد آلية. تستخدم الطابعة ثلاثية الأبعاد لصنع مجسمات صلبة ثلاثية الأبعاد. وقد قام بتصنيعها اثنين من خريجي كلية الهندسة لعام ٢٠١٧ محمد أشرف الشربيني وعبد الله العجوز من قسم الميكاترونكس.
 تبدأ عملية الطباعة باستخدام هذه الطابعة عن طريق خلق مجسم ثنائي الأبعاد تم تصميمه بمساعدة الكمبيوتر. ثم تتم معالجة الصورة ثنائية الأبعاد وتحويل النموذج إلى طبقات رقيقة مختلفة. ثم تطبق الطابعة الأوامر التي أصدرت لها على الطبقات الرقيقة المتنوعة لوضع طبقات متتالية من المواد عبر فوهة طباعة تسمى الطارد (extruder). يتحرك الطارد من خلال محوره لطباعة طبقة فوق طبقة لإنشاء النموذج الثلاثي الأبعاد.
تبدأ عملية الطباعة باستخدام هذه الطابعة عن طريق خلق مجسم ثنائي الأبعاد تم تصميمه بمساعدة الكمبيوتر. ثم تتم معالجة الصورة ثنائية الأبعاد وتحويل النموذج إلى طبقات رقيقة مختلفة. ثم تطبق الطابعة الأوامر التي أصدرت لها على الطبقات الرقيقة المتنوعة لوضع طبقات متتالية من المواد عبر فوهة طباعة تسمى الطارد (extruder). يتحرك الطارد من خلال محوره لطباعة طبقة فوق طبقة لإنشاء النموذج الثلاثي الأبعاد.
يقول محمد الشربيني: “هذه الطابعة ثلاثية الأبعاد تستخدم تقنية (“Stereolithography “SLA). ويمكنها في الغالب إنتاج أي تصميم ومن ثم يمكنها أن تصنع العديد من الأشياء مثل النماذج الأولية للمنتجات ولفافات الطعام والإكسسوارات ولعب الأطفال وديكورات المنزل وغيرها الكثير. “


 أما المشروع الثاني عبارة عن يد آلية (ROBOQA) يتم التحكم فيها عن طريق وحدة تحكم (LeapMotion). تقوم هذه اليد بمحاكاة حركة اليد البشرية دون ربط أي مجسات بيد الإنسان نفسها. صاحب فكرة المشروع محمد عماد لطفي خريج كلية الهندسة لعام ٢٠١٧ قسم الميكاترونكس وتم تصميم أجزاؤه باستخدام الطابعة ثلاثية الأبعاد المذكورة أعلاه.
أما المشروع الثاني عبارة عن يد آلية (ROBOQA) يتم التحكم فيها عن طريق وحدة تحكم (LeapMotion). تقوم هذه اليد بمحاكاة حركة اليد البشرية دون ربط أي مجسات بيد الإنسان نفسها. صاحب فكرة المشروع محمد عماد لطفي خريج كلية الهندسة لعام ٢٠١٧ قسم الميكاترونكس وتم تصميم أجزاؤه باستخدام الطابعة ثلاثية الأبعاد المذكورة أعلاه.
تستند فكرة ROBOQA على تلقي إشارة من اليد البشرية ونقلها إلى اليد الآلية من خلال وحدة التحكم. تقوم وحدة التحكم بتحويل حركات اليد البشرية إلى نموذج ثلاثي الأبعاد. يتلقى لوح ال Arduino Uno تلك القراءات وينقلها إلى المحركات الست المتصلة بها والتي تبدأ في التحرك وفقًا لذلك. تتحكم خمسة محركات في أصابع اليد الآلية بينما يقوم المحرك المتبقي بتدوير المعصم.
يقول محمد عماد لطفي مطور ROBOQA “هذه اليد الآلية هي الأولى من نوعها التي يتم تطويرها في مصر. كل الأيدي الآلية التي تم تطويرها سابقاً كانت بحاجة إلى ربط المجسات باليد البشرية لإرسال إشارات إلى اليد. ومع ذلك يمكن لـ ROBOQA أن تحاكي عن بعد حركات اليد البشرية دون الاستعانة بأية مجسات”.

[:]


